Using NetworkX to find all nodes/edges reachable from a given node and rank by path length
Find all of the nodes reachable from a given node
We can use shortest_path() to find all of the nodes reachable from a given node.
Alternatively, there is also descendants() that returns all nodes reachable from a given node (though the document [1] specified input G as directed acyclic graph.
First we create a sample graph (directed):
import networkx as net # version 2.5
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create a sample graph
g = net.DiGraph()
net.add_path(g, ['A','B','C'])
net.add_path(g, ['A','C','D'])
net.add_path(g, ['A','E','F'])Plot it:
net.draw(g, with_labels=True, node_color='yellow')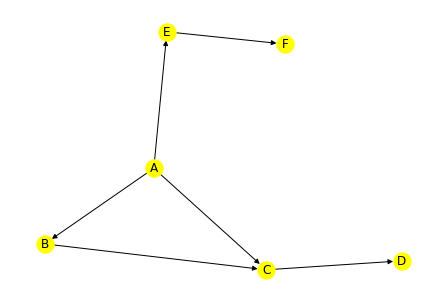
To illustrate, we find all nodes connected to 'B' (the output will include 'B'):
nodes = net.shortest_path(g,'B').keys()
print(nodes)Output:
dict_keys(['B', 'C', 'D'])Alternatively, use descendants(G, source):
net.descendants(g, 'B')Output:
{'C', 'D'}Now let's see the undirected graph case:
u = g.to_undirected()
net.draw(u, with_labels=True, node_color='yellow')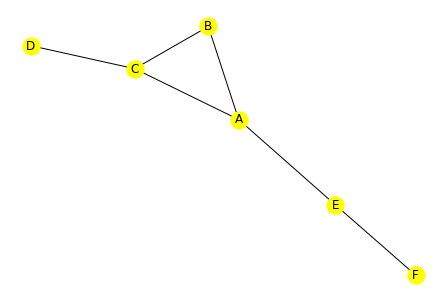
We find all nodes connected to 'B' ('B' still in output):
# Get a list of nodes reachable from the given node 'B' (included).
nodes = net.shortest_path(u,'B').keys()
print(nodes)Output:
dict_keys(['B', 'A', 'C', 'E', 'D', 'F'])Find all of the edges reachable from the given node
We first create a subgraph containing all the reachable nodes found above:
Directed graph case:
s = g.subgraph(nodes) print(s.edges())Output:
OutEdgeView([('A', 'B'), ('A', 'C'), ('A', 'E'), ('B', 'C'), ('C', 'D'), ('E', 'F')])Or do it in one line:
s = g.subgraph(net.shortest_path(g.to_undirected(),'B')) print(s.edges())Output:
OutEdgeView([('A', 'B'), ('A', 'C'), ('A', 'E'), ('B', 'C'), ('C', 'D'), ('E', 'F')])Undirected graph case:
s = u.subgraph(nodes) s.edges()Output:
EdgeView([('A', 'B'), ('A', 'C'), ('A', 'E'), ('B', 'C'), ('C', 'D'), ('E', 'F')])
Find the distance from a given node to all other nodes reachable (using undirected graph case as an example)
We can use shortest_path_length() to compute shortest path lengths in the graph and therefore calculating the distance.
# Specify both source and target
print(net.shortest_path_length(u, source = 'B', target = 'F'))
# Specify source
print(net.shortest_path_length(u, source = 'B'))
# Specify target
print(net.shortest_path_length(u, target = 'E'))
# Source,target not specified
P = dict(net.shortest_path_length(u))
POutput:
3
{'B': 0, 'A': 1, 'C': 1, 'E': 2, 'D': 2, 'F': 3}
{'E': 0, 'A': 1, 'F': 1, 'C': 2, 'B': 2, 'D': 3}
{'A': {'A': 0, 'B': 1, 'C': 1, 'D': 2, 'E': 1, 'F': 2},
'B': {'A': 1, 'B': 0, 'C': 1, 'D': 2, 'E': 2, 'F': 3},
'C': {'A': 1, 'B': 1, 'C': 0, 'D': 1, 'E': 2, 'F': 3},
'D': {'A': 2, 'B': 2, 'C': 1, 'D': 0, 'E': 3, 'F': 4},
'E': {'A': 1, 'B': 2, 'C': 2, 'D': 3, 'E': 0, 'F': 1},
'F': {'A': 2, 'B': 3, 'C': 3, 'D': 4, 'E': 1, 'F': 0}}Reference
- [1] https://networkx.org/documentation/stable/reference/algorithms/generated/networkx.algorithms.dag.descendants.html
- [2] https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13914920/networkx-extract-the-connected-component-containing-a-given-node-directed-grap/
- [3] https://networkx.org/documentation/stable/reference/classes/generated/networkx.Graph.subgraph.html
- [4] https://networkx.org/documentation/stable/reference/algorithms/generated/networkx.algorithms.shortest_paths.generic.shortest_path_length.html